Granting read-only access to kubenav
This blog article shows how to grant read-only access to kubenav using a service account and RBAC permissions.
What is kubenav?
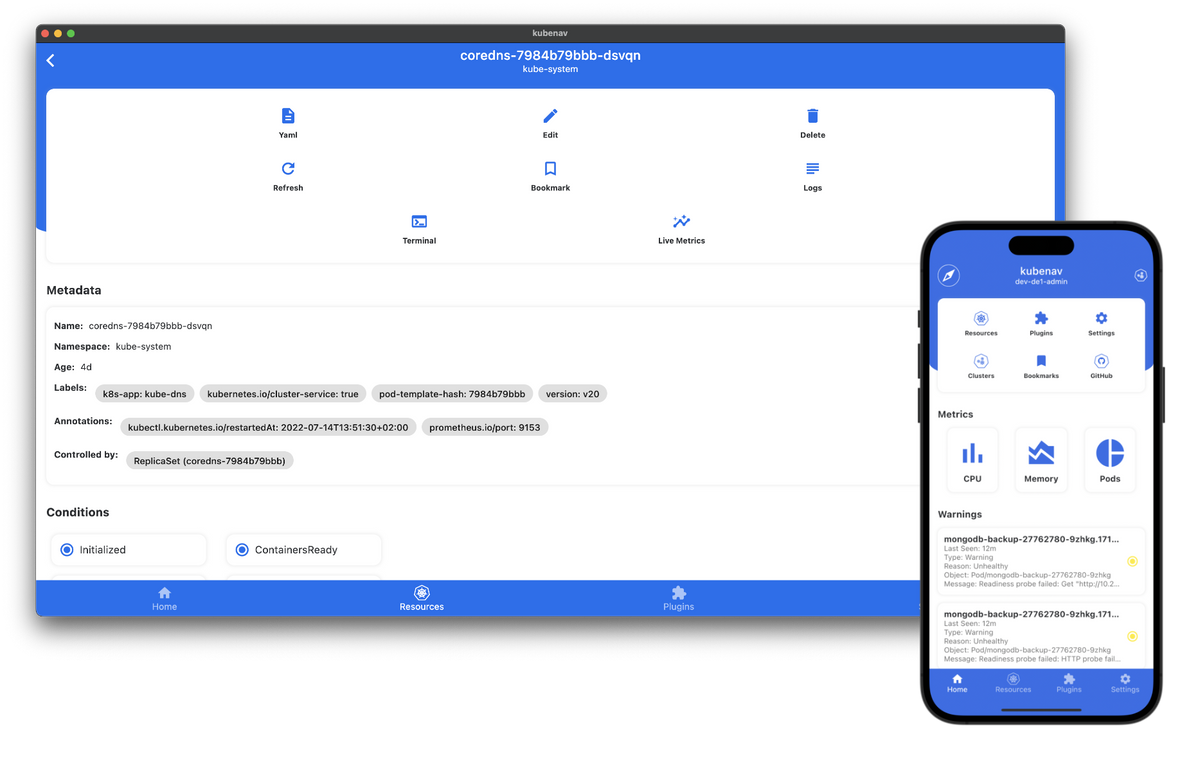
Kubenav is an open-source mobile application that provides a user-friendly interface for managing and monitoring Kubernetes clusters. It allows users to interact with Kubernetes resources, view cluster health and performance metrics, and perform various management tasks from their mobile devices. Kubenav is designed to simplify Kubernetes cluster management and make it more accessible to users who prefer using mobile devices.
Setting up Kubernetes
Creating the Namespace
kubectl create namespace kubenavapiVersion: v1
kind: Namespace
metadata:
name: kubenavCreating the ServiceAccount
kubectl create serviceaccount kubenav --namespace kubenavapiVersion: v1
kind: ServiceAccount
metadata:
name: kubenav
namespace: kubenavCreating the ClusterRole
apiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRole
metadata:
name: kubenav-readonly
rules:
- apiGroups: ["*"]
resources: ["*"]
verbs: [get,list]Creating the ClusterRoleBinding
kubectl create clusterrolebinding kubenav --serviceaccount=kubenav:kubenav --clusterrole=kubenav-readonlyapiVersion: rbac.authorization.k8s.io/v1
kind: ClusterRoleBinding
metadata:
name: kubenav
roleRef:
apiGroup: rbac.authorization.k8s.io
kind: ClusterRole
name: kubenav-readonly
subjects:
- kind: ServiceAccount
name: kubenav
namespace: kubenavSetting up the kubeconfig
The view-serviceaccount-kubeconfig plugin for kubectl can be used to easily generate a kubeconfig file that allows you to authenticate and access a Kubernetes cluster using the token of a specific service account.
Installing the plugin
kubectl krew install view-serviceaccount-kubeconfigkrew installed yet, checkout my tutorial here.Creating the kubeconfig
Until Kubernetes v1.24, whenever you create a service account in Kubernetes, it is assigned a token that can be used for authentication. This behavior has been changed because of security issues in the latest versions of Kubernetes.
Therefore we first have to create a token for the service account kubenav using the kubectl create token command. This token then can be used to generate a kubeconfig file called config-for-kubenav with the following one-liner:
kubectl create token kubenav --namespace kubenav | kubectl view-serviceaccount-kubeconfig > config-for-kubenavThe kubeconfig should look like this:
apiVersion: v1
clusters:
- cluster:
certificate-authority-data: <CA_OF_CLUSTER>
server: https://<IP_OF_API_SERVER>:<PORT_OF_API_SERVER>
name: <NAME_OF_CLUSTER>
contexts:
- context:
cluster: <NAME_OF_CLUSTER>
user: kubenav
name: kubenav
current-context: kubenav
kind: Config
preferences: {}
users:
- name: kubenav
user:
token: <TOKEN>This kubeconfig file can now be used in kubenav to authenticate against your Kubernetes cluster.
Making your life easier
Of course, I also have created a Helm chart that bootstraps the required resources. You can find it on ArtifactHub: